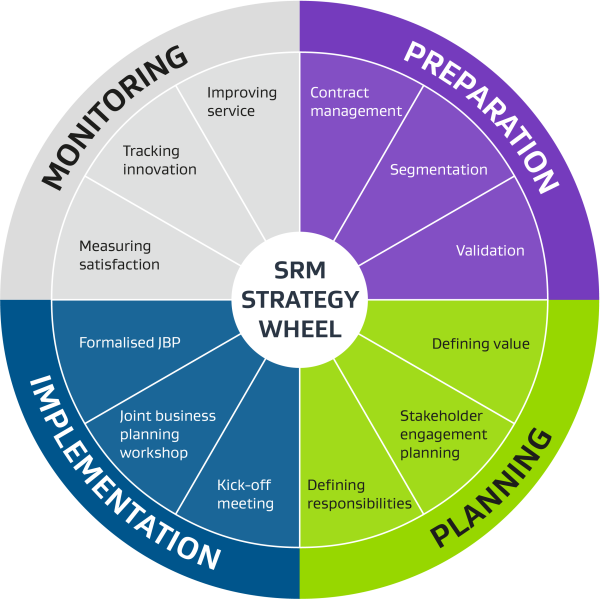
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) aims to build a collaborative and long-term partnership with suppliers. This benefits the customer and the supplier/provider by minimising cost, optimising delivery, and making each party more resilient against potential risks to supply.
The tools and templates on this page will help build this partnership. A successful SRM strategy often requires a business change and senior stakeholder endorsement.
If you need advice on this or any other aspects of SRMs, contact us.
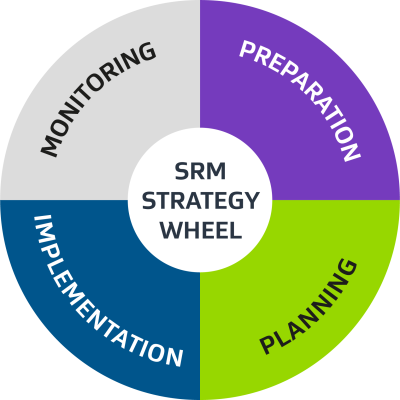
SRM strategies/plans can look different for every supplier/tier, depending on your organisation.
This page provides a holistic view of a complete SRM strategy or click to activities and their corresponding tools/templates for more guidance.
The focus in the preparation phase is gathering relevant documents and data. This will help identify the suppliers where SRM would be most valuable. The 3 steps which make up the preparation phase are highlighted in purple in the wheel below.
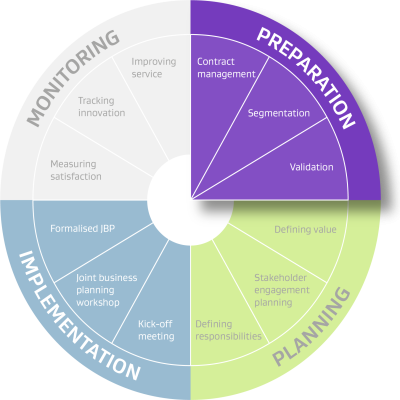
A contract register is essential for effective contract management, and contract management is essential for an SRM strategy. You risk losing visibility and control over key agreements without a clear view of each contract, their scope, the parties involved, and their deliverables. This lack of oversight makes it difficult to manage costs, assess supplier performance, and ensure compliance.
A well-maintained contract register is the foundation of efficiency, accountability, and strategic planning for SRM and broader business operations.
For organisations with a large supplier base, segmentation is a two-step process:
If your smaller business entity/agency has a clear view of the categories that your suppliers fall into, and it has a smaller supplier base, you may not need to complete category segmentation. You may find the Lite segmentation tool useful instead.
Validate your segmentation results with the appropriate internal stakeholders before moving onto the planning phase. You could do this by holding an internal meeting to discuss your thinking and approach so far. Their feedback may adjust segmentation results. Finally, it’s good practice to secure sign-off on the agreed strategic suppliers. Approval steps:
This phase of the SRM strategy defines the anticipated value of an SRM plan for specific suppliers. This in turn informs your engagement and scope of roles/responsibilities.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach and plans should be appropriate for the tier of the supplier. Tier 4 suppliers won’t require the same level of engagement as tier 1 suppliers.
The 3 steps which make up the planning phase are highlighted in green in the wheel below.
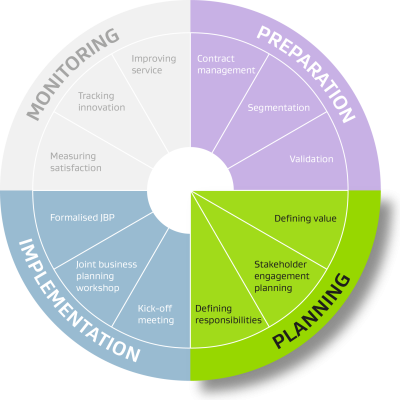
Identifying SRM value opportunities improves efficiency by defining goals and establishing allocation of time and resources. It also reinforces buy-in for the SRM project from external and internal stakeholders. This is a key step for identifying what outcomes you want and expect from the project.
Good stakeholder engagement comes from stakeholder analysis and a well-informed communications plan. This step is key to informing expectations around support for the SRM project both internally and externally. An effective communications strategy can help to maximise this support.
Once you understand stakeholders’ expectations, the next step is to clarify roles and responsibilities. Create a plan of who does what in the SRM project by drafting a high-level RACI chart. This will later be presented to stakeholders for them to agree to as part of the implementation phase.
This phase of the SRM strategy mobilises the SRM project by initiating the pre-planned external engagements with suppliers and formalising the Joint Business Plan, a document which guides the relationship going forward.
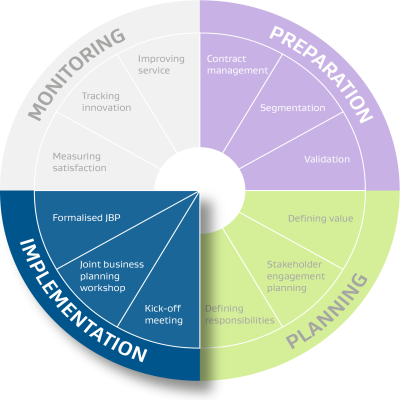
The 3 steps which make up the implementation phase are highlighted in blue in the wheel below.
Following segmentation and planning, your internal SRM project group should have some proposed supplier-specific initiatives. A kick-off meeting should secure support for the initiatives from supplier/providers. Having a structured agenda in place ahead of this meeting will help you to approach it with confidence and clarity.
A joint business planning workshop led by the project leads from both the customer/agency and the provider/supplier will help you finalise a formal Joint Business Plan (JBP). The purpose of this workshop is to communicate strategic goals for the project and brainstorm where the two organisations can align. From here, a JBP can be drafted and signed. The JBP informs the working relationship moving forward.
This phase of the SRM strategy monitors the established supplier relationship by keeping track of satisfaction on both the customer and the supplier/provider side. The activities chosen in this phase will depend on how the relationship is performing. If it is going well, you can begin to seek innovation. If it is under-performing, you can opt for a service improvement plan instead.
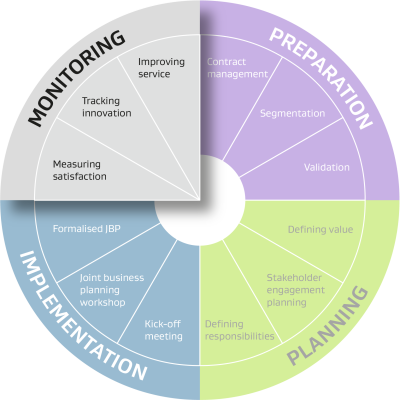
Once the SRM strategy is in place with a supplier/provider, it is a good idea to measure how the relationship is performing. Complete this scorecard collaboratively with the supplier/provider to get a balanced picture of satisfaction.
Seeking innovation comes after following a formalised JBP and measuring satisfaction via the balanced scorecard. Innovation tracking lets you capture ideas, evaluate their value, identify risks and plan an implementation approach.
Use the SIP template to initiate and monitor improved performance expectations if you find that despite implementing an SRM strategy, your supplier/provider is not meeting the expected standard for specific deliverables.